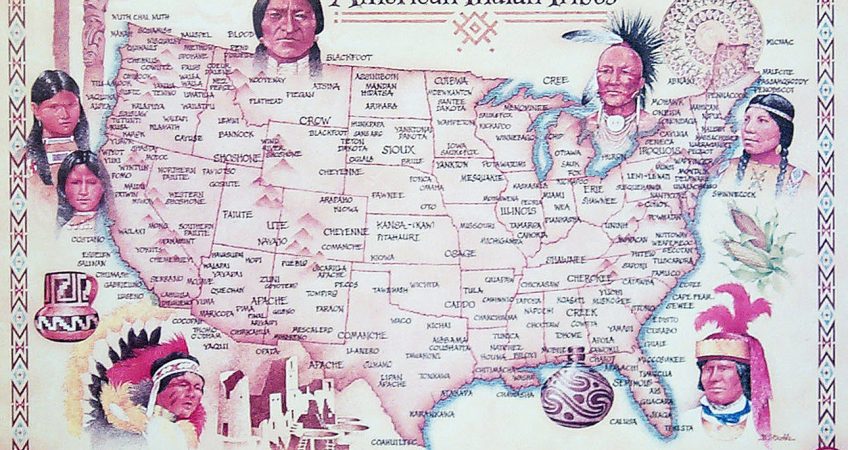
Popular Indian Tribes In The United States Of America
The United States is home to some 567 Native American tribes according to latest statistics from the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA). Out of these, some are popular for their size, language, heritage and culture.
Undoubtedly, Navajo is the largest and the most popular Indian tribe in the US with a population of around 340,000 and around 200,000 speakers of the Navajo language.

Officially known as the Navajo Nation, this tribe inhabits an area of approximately 71,000 km2 which spans over three states; Utah, Arizona, and New Mexico. The geographical borders of the reservation were established in 1868 by the Navajo Treaty. Their tradition and culture is rooted in their oral history and the governance is organized around clans. Clans were predominantly matrilineal and gained social status from the mother. They resisted western education from the beginning and educated their children in the community head start programs. The capital of the Navajo Nation is the Window Rock, named after the graceful rock formation.
Cherokee, the second most populous Native American tribe in the US has a population of around 316,000 and has a well preserved language which belonged to the Iroquoian languages family. Eastern Band, United Keetowah Band, and the Cherokee Nation are the legally recognized bands of the tribe. Historically, the Cherokees consisted of a religious and priestly elderly group and younger group who took on warfare. They considered war a polluting activity and the warriors had to purify themselves before being reintegrated to the tribe. Cherokees were agrarian from the early days and lived in fixed villages.
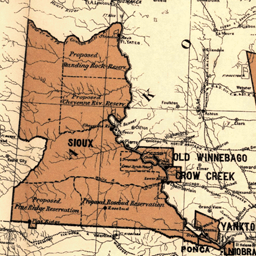
The third most populous and one of the most popular tribes is the Sioux or commonly referred to as the Great Sioux Nation which has a population of around 170,000. The Sioux has three major tribes based on the language they speak; Nakota, Lakota, and Dakota. The name Sioux is abbreviated from Nadouessioux which roughly means “Little Snakes”. Sioux people are known for their warrior and hunting culture. They hunted buffalo on horseback and relied heavily on buffalo fur trade. Also, they were known for waging wars against the US Army, The Great Sioux War of 1876 being the most noted. Inhabiting the source of the Mississippi river in the 17th century, they were confined mostly to the Pine Ridge Indian Reservation after 1876.
Chippewa or Ojibwe is the fourth most populous Native American tribe with a population of around 170,000 within the US. A portion of the Chippewa population lives in Canada as well. They traditionally speak the Ojibwe language which belongs to the Algonquian family. Ojibwe people are known for copper mining and trading, birch back canoes, and wild rice cultivation. Also, they kept detailed scrolls of oral history, maps, songs, stories, mathematics, and geometry.
They usually live in bands and have a sedentary lifestyle while hunting and fishing in addition to the squash and maize cultivation.
Choctaw is the next most populous tribe with around 160,000 members totally. They are considered descendants of the Mississippi and Hopewell cultures who inhabited the east of the Mississippi river. The Choctaw has three distinct divisions; Southern, Western, and Eastern. They never waged war against the US and didn’t take part in wars which made the Euro-Americans call them one of the “Five Civilized Tribes.” However, they too were forced from their homelands as part of the Indian Removal Act. The Choctaw were agrarian and worked communally to share their harvests. They wore handmade colorful clothes based on their ancestral designs. They spoke Choctaw language which was a Muskogean language.
The next popular tribe is the Apache with a population of approximately 111,000. They inhabit the South-Western US and are consisted of six sub divisions; Lipan, Chiricahua, Plains, Jicarilla, Western Apache, and Mescalero. These Apaches are independent and spoke about five different languages. They are known for fighting the Mexican and Spanish who invaded them and were famous as fierce fighters and skilled war strategists.
